The Value of Respiratory Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation in Pulmonary Rehabilitation of COPD Patients
Author: X.Zhao (RICU& Sleep Center, Tianjin Chest Hospital), Y.Li (Pulmonary and critical care medicine. Tianjin Chest Hospital), G.Li (RICU& Sleep Center, Tianjin Chest Hospital, B.Li(Respiratory & Critical Care Medicine, Tianjin Chest Hospital), X. Hu (Respiratory & Critical Care Medicine, Tianjin Chest Hospital), X. Yang(Respiratory & Critical Care Medicine, Tianjin Chest Hospital), J.He (Tianjin Fourth Central Hospital).
Objective
To investigate the rehabilitation value of respiratory neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation. In Pulmonary Rehabilitation of COPD patients.
Method
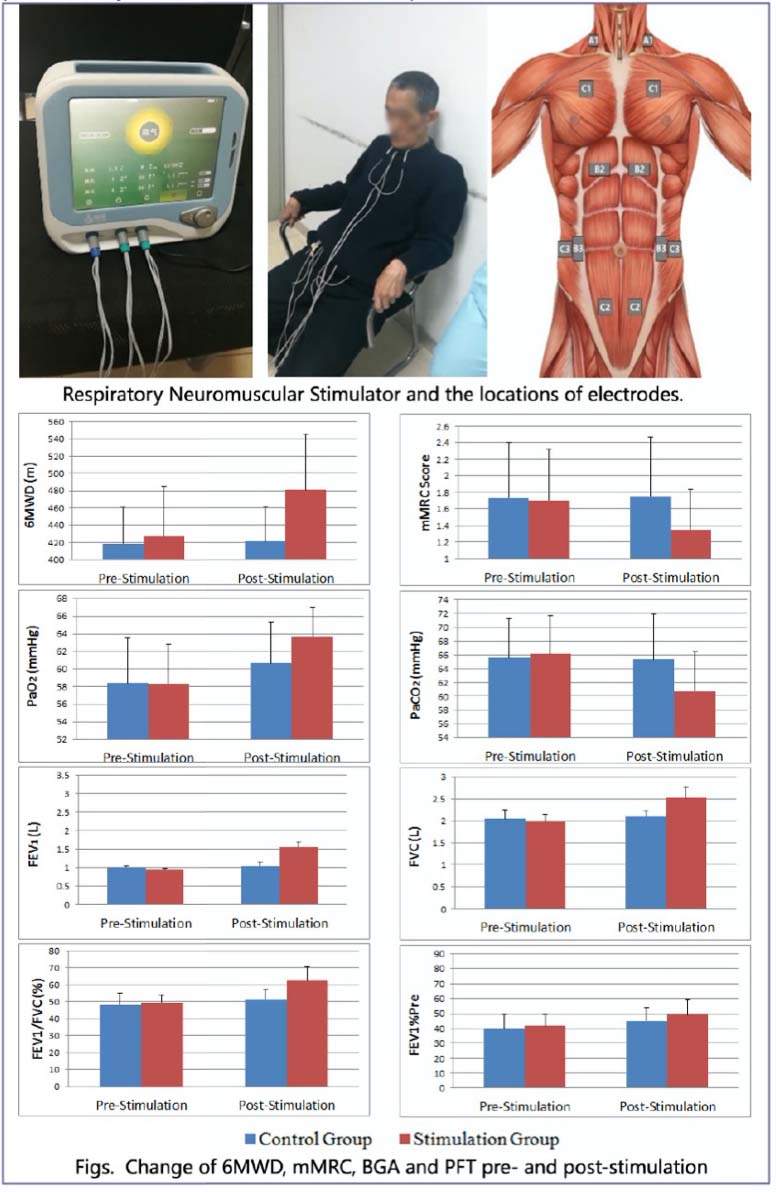
126 patients (85 males and 41 females) with stable Grade-D CODP to GOLD2017 guideline were involved in the RCT study. All cases were divided into stimulation group(n=63) and Control Group(n=63). All patients were given oxygen therapy, theophylline LAMA, LABA, ICS, and another needed drugs regularly. Moreover, the stimulation group patients were treated with ResPower Respiratory Neuromuscular Stimulator EDAP06 (Yaguo Technology Ltd, Beijing China), the current intensity was 5-15mA, stimulation frequency was 40-50Hz, once a day for 30 minutes, and totally for 12 weeks. One pair of phrenic nerve electrodes were attached to 1/3 of the lateral of the Sternocleidomastoid muscle on both sides respectively, and the reference electrodes were attached to the surface of the pectoralis major muscle. There were two pairs of abdominal muscle electrodes, one pair were symmetrically placed on the surface of the anterior rectus abdominis, reference electrodes were 30cm inferior to it; the other pair of electrodes were placed on the surface of the bilateral Oblique Abdominis, and the reference electrode were 10cm lateral to it. Synchronizing with the electrical stimulation, patients should actively inhale or exhale following the voice indication. The 6-minute walking distance(6MWD), mMRC score, pulmonary function teste (PFT), blood gas analysis (BGA) were performed to the other group’s patients.
Results
There was no significant difference in 6 MWD,mMRC,PFT and BGA on baseline between the two groups. After 12 weeks of electrical stimulation, 6 MWD in the stimulation group was significantly lower than that baseline(P<0.001), and there was no change in the control (P<0.05). Post-stimulation mMRC in the stimulation group was significantly lower than that pre-stimulation (P<0.001), and there was no change in the control. PaO2 in the stimulation group was significantly higher than the pre-stimulation(P<0.05) and PaCO2 got a decrease (P<0.05), however the PaO2 and PaCO2 in the control group had no significant changes(P>0.05). After 12 weeks ‘stimulation, FEWV1, FVC, FEV1/FVC and FEV1%Pre in the stimulation group were significantly increased compared with those pre-stimulation (P<0.001), while no statistical change in the control.
Conclusion
Combines stimulation of phrenic nerve and abdominal muscles can significantly improve the 6MWD of grade-D COPD patients, improve their pulmonary ventilation function and blood gases, which means that it can improve life quality and respiratory function of these patients, which is of great value for pulmonary rehabilitation of COPD patients.