COVID-19 Clinical Report for Dead Infected Case
On February 25, MedRxiv published a paper from Wuhan University People's
Department of infection, People's Hospital of Wuhan University.
coronavirus pneumonia patients died of severe inflammatory cascade.
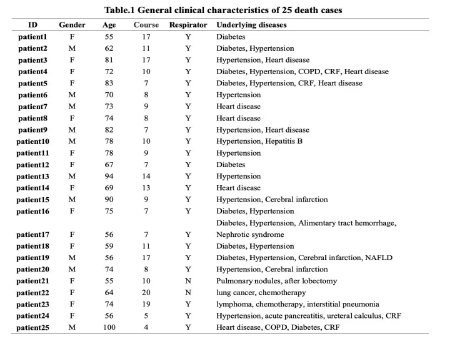
General clinical characteristics of 25 dead patients: all of them have basic diseases, including 16 cases of hypertension, 10 cases of diabetes, 8 cases of heart disease,
5 cases of kidney disease, 4 cases of cerebral infarction, 2 cases of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, 2 cases of malignant tumor, 1 case of acute
pancreatitis . Graphs of MedRxiv
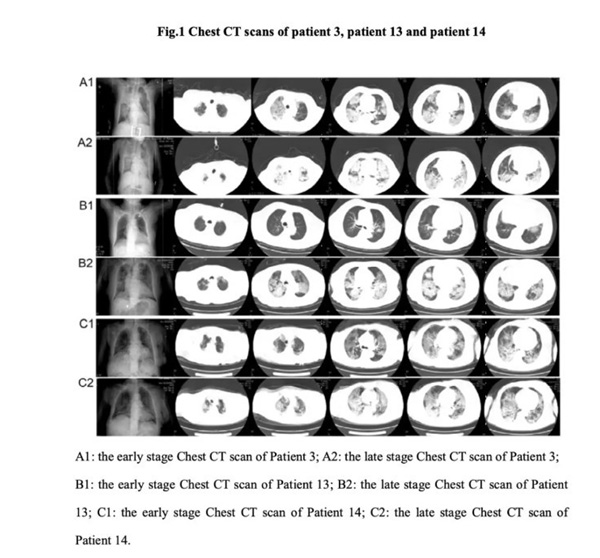
A1 and A2, B1 and B2, C1 and C2 were the early and late chest CT scans of three patients respectively
The novel coronavirus pneumonia is the most common organ damage in lung and heart, followed by kidney and liver. The novel coronavirus pneumonia is the most important risk factor for death in patients with new corona pneumonia. Besides, bacterial infection may also be an important factor to accelerate the death of patients. Malnutrition is common in critically ill patients.
For novel coronavirus pneumonia patients who died of respiratory failure in the study, Gong Zuojiong, a correspondent, told DeepTech deep technology interview that these patients were suffocated because there was a lot of mucus in the lungs, oxygen could not enter the alveoli and gas exchange, oxygen absorption could not be absorbed, and finally suffocated. The course of the disease is related to many factors, including the way and timing of respiratory support, early warning, and of course, the severity of the underlying disease. Now we need to establish an early warning evaluation system, so as to be able to intervene earlier and more actively, so as to reduce the mortality rate.
The novel coronavirus pneumonia and respiratory failure were diagnosed as clinical death causes. The same findings were also reported by Professor Liu Liang of the Department of forensic medicine of Tongji Medical College of Huazhong University of Science and Technology and his team's anatomy of the dead body of the new corona pneumonia.
Zhong Nanshan, senior member of the National Health Protection Committee and academician of China Academy of engineering, mentioned that in the new corona pneumonia, mucus removal in small airway is an important research objective. The novel coronavirus pneumonia is the most common organ damage in lung and heart, followed by kidney and liver. The novel coronavirus pneumonia is the most important risk factor for death in patients with new corona pneumonia. Besides, bacterial infection may also be an important factor to accelerate the death of patients. Malnutrition is common in critically ill patients.
General anatomy report of novel coronavirus pneumonia death corpse system was reported by Liu Liang team in the Journal of forensic medicine. The content of this report is a case of gross observation of systematic autopsy.
The research team pointed out that the lung injury of the dead was obvious, the lung was patchy, gray white focus and dark red bleeding were seen, and a large number of thick secretion overflowed from the alveoli in the section, suggesting that the new coronavirus mainly caused the inflammatory reaction characterized by deep airway and alveoli injury. The case with multiple cerebral infarction was diagnosed as novel coronavirus on the thirteenth day after admission, and his test on nucleic acid is positive. The novel coronavirus pneumonia and respiratory failure were diagnosed as the cause of clinical death on the 28th day after admission.
Novel coronavirus pneumonia has a prominent feature: mucus in the small airway is very high, and the viscosity is very high, which obstruct airway patency, which causes secondary infection and more serious." Novel coronavirus pneumonia was a major research topic in February 27th. At the February 27th Guangzhou Medical University held the special news briefing on epidemic prevention and control, Zhong Nanshan, senior member of the National Health Protection Committee and academician of China Academy of engineering, mentioned that in the new corona pneumonia, mucus removal in small airway is an important research object.
Appendix
Liu Liang and his report- General anatomy report of novel coronavirus pneumonia death corpse system
Recently, the official website of the Journal of Forensic Medicine updated and released the topic of autopsy of the new type of coronavirus pneumonia. The results of the report showed that, from the gross observation of the autopsy, the deceased's lung injury was obvious, white foam-like mucus was seen in the trachea, and jelly-like mucus was observed in the right lung bronchus. A large number of sticky secretions were seen from the lungs Spilled and visible fiber strands. This latest discovery has made the treatment of sputum excretion of new coronary pneumonia the focus of attention.
Professor Liu Liang said in an interview with reporters: "We did find some mucus secretions on the section of the lungs of the deceased under the microscope, which can remind clinical treatment to be vigilant. At present, the alveolar function may be damaged. The tract is blocked by mucus, and the clinical manifestation of hypoxia will occur. Therefore, to improve the human hypoxia and maintain the airway patency, the mucus must be diluted or dissolved. In clinical treatment, if the mucus components are not resolved, the way of oxygen supply purely may not achieve the purpose, and sometimes it will have an adverse effect. Positive pressure oxygen may push the mucus deeper and wider, which will increase the patient's hypoxia.

Liang Liu, a professor of forensic pathology at Tongji Medical College of Huazhong University of Science and Technology, was interviewed
Recently, a media report said: "A large number of sputum plugs appeared in the lungs of the deceased, and the sputum plugs were generated by the use of a ventilator, which caused people to die of hypoxia. Starting yesterday, the emergency was switched to a sputum suction machine to help Wuhan. The death
toll has been halved, thanks to the efforts of the donors and the team of Professor Liu Liang from the Department of Forensic Medicine of Tongji. "For this report, experts said:" The sputum plugs are not caused by the ventilator, but are formed by mucus lesions in the lungs. It is a pathological process after disease damage. "
The role of expectoration is undoubted. Experts also emphasized the importance of deep expectoration in related interpretations, but this does not conflict with respiratory support. The combination of respiratory support and expectoration is the best solution. However, the current commonly used sputum expulsion methods require disconnecting the ventilator and cannot work with the ventilator, which may cause a series of complications and the risk of infection by medical staff.
Intelligent bionic expectoration is an innovative expectoration technology, which can achieve synchronous closed expectoration with invasive mechanical ventilation. It is a new technology that intelligent bionic expectoration is used to clear deep lung and airway secretion of patients with invasive mechanical ventilation. The system simulates the principle of physiological cough, connects with the ventilator air path and the patient through a set of specially designed pipeline, and can work in parallel with the ventilator in time: in the inspiratory phase, the ventilator supplies air to the patient normally; in the expiratory phase, the intelligent bionic sputum
drainage system takes the sputum out with high-speed air flow; and monitor- s the patient's breathing state in real time through multiple sensors to
ensure the sputum drainage and mechanical communication Gas synchroniza tion, to achieve online, on-invasive, closed, synchronous, safe and efficient
expectoration.
The potential benefits of intelligent bionic sputum drainage system in pneumonia patients include:
Safe, non-invasive discharge of lung deep secretions, improve the cure rate;
Closed expectoration can reduce the risk of infection;
Novel coronavirus pneumonia samples can be detected by deep discharge from the lungs, and the high-risk sampling operation such as
Broncho alveolar lavage is reduced.




